This defaults Taxes and automatic calculation at the transaction line level. Tax Categories would be applicable to the transaction and the Tax Base Amount calculation would be determined.
Navigation
India Local Purchasing→ India Localization → Setup → Tax Setup → Tax Category
Defining Tax Categories
1. Navigate to the tax Category India Localization window as shown below.
2. Now define a Tax Category for Basic Excise Duty @ 8% and VAT @ 12.5% as shown below
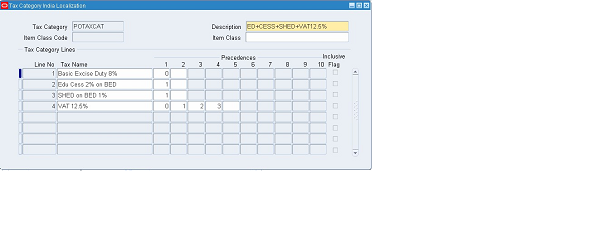
3. The meaning for the fields are given below –
• Tax Category – Enter a Unique name for the tax category. The Tax Category Name should be Suggestive so that the User should be able to identify the applicability of the Tax Category
• Description – Enter a meaningful full description for the tax category you define. This should describe the tax category name in detail.
• Tax Name – Use this column to enter tax names from LOV. You can associate any number of tax names to a Tax category. A tax name can be associated with any number of tax categories; however, you cannot use the same tax name more than once in a Tax Category. The tax rate applicable on the transaction date will be applicable for that transaction.
• Tax Precedence 1- 10 – Precedence refers to the manner in which the tax will be applied. The tax rate may be applied on the transaction base value or on another tax line or compounding them or a combination of all. The base amount or material sale value is by default given a precedence value of ‘0’. The subsequent precedence is assigned to the tax names’ respective Line Numbers. A maximum of ten levels of precedence is permitted.
The Taxes included in Tax Category would default on a transaction line. But, you would also have a provision to add new tax lines manually.
If a tax name is defined as ‘Adhoc’ then the Precedence has no Relevance in tax computation of such tax, however, calculation of other taxes can be based on this tax. For ‘Adhoc’ taxes users needs to enter the value manually.
A tax cannot be dependent on itself. However, interdependent taxes can be set up in precedence e.g. tax at line 1 can depend on tax at line 2. Similarly, tax on line 2 can depend on tax at line 1.
In the above example, in the first line i.e. against Basic Excise Duty 8% ‘0’ is defined. This means that the tax amount is being calculated on the base amount only. In the second line against EDU Cess on BED 2%, ‘1’ is defined. Thus the tax is being calculated on Basic Excise Duty only which is at Line ‘1’. For SHED on BED 1%, ‘1’ is defined. So tax gets calculated on Basic Excise Duty only. Against VAT 12.5% , ‘0’, ‘1’, ‘2’, , ‘3’ is defined. Thus tax is being calculated on the Base amount, Basic Excise Duty, EDU Cess on BED, and on SHED on BED.
Other Related Articles
DEFINE BUYERS
DEFINE APPROVAL GROUP
APPROVAL ASSIGNMENT
APPROVAL HIERARCHY
NUMBERING SEQUENCE ASSIGNMENT
REQUISITION TEMPLATE
ITEM CATEGORIES
OPEN AND CLOSE PURCHASING PERIODS